
What are the Gaps?
Many students, parents, and teachers encounter challenging gaps within the current education system. Guardian Airwaves LLC aims to address and reduce these gaps by providing targeted product solutions.

ADHD diagnoses are rapidly rising.*
25.1 million youths (12-17 ages) in the U.S. make up our Middle School and High School student body.**
7.1M youths have been diagnosed with ADHD. 5.5M of these diagnosed with ADHD had at least one co-occurring disorder such as learning disability, conduct disorder, anxiety, depression, and speech problems.***
Besides these personal struggles, students and their families are faced with the following:
- Achievement Gaps
- Teacher Shortages & Inequities
- Unequal Access to Higher Education
- Curriculum Gaps
- Social & Emotional Learning (SEL)
- Technology Gaps
- Special Education Needs
- Lack of Vocational Education Opportunities
- Language Barriers among migrant or international students
*CDC reported that in 2022, over 7 million (11.4%) U.S. children aged 3-17 years were diagnosed with ADHD, an increase of 1 million compared to 2016
**https://www.childstats.gov/americaschildren/tables/pop1.asp
***2022 National Survey of Children’s Health

ADHD may be a significant risk factor for developing smartphone addiction. Excessive smartphone use has been associated with numerous psychiatric disorders.****
****https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6408841/
Overall Neurodevelopmental Disorders (NDDs)
Approximately 15-20% of the general population exhibits some form of neurodivergence. Among 3-17 year olds in the United States (2019-2020) the average is:
- ADHD: 8.5% (6.3 Million)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): 2.9% (2 Million)
- Intellectual Disability: 1.4% (1 Million)
- Learning Disability: 6.4% (4.53 Million)
“About 1 in 9 kids in the U.S. have been told by a doctor at some point that they have ADHD (that’s around 7.1 million kids), and about 1 in 10 kids (6.5 million) still have ADHD now. Of those kids who currently have ADHD:
-
More than half (58%) have moderate or severe symptoms.
-
More than three-quarters (78%) also have another condition, like anxiety, learning problems, or depression.
-
About half (54%) take ADHD medicine.
-
Almost half (44%) got behavioral therapy in the last year.
-
Nearly one-third (30%) didn’t get any ADHD-specific treatment.”*****
About 67% of kids with ADHD have emotional and mental health conditions along with their ADHD.
*****https://www.cdc.gov/adhd/data/index.html

Majority of U.S. States are in Need
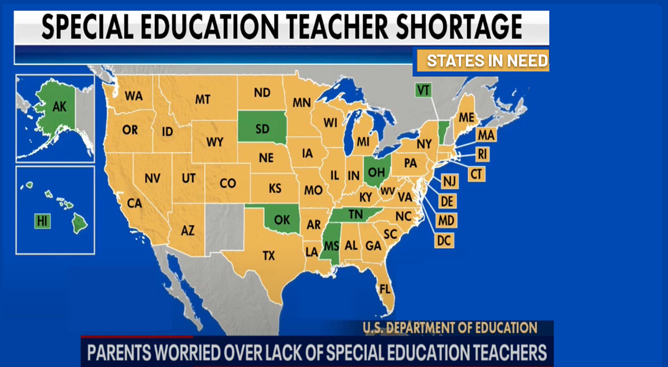
The majority of US states in yellow are in great need for support for their kids but yet there is a huge shortage of special ed teachers due to burnout, heavy workloads and now non-existent budgets. Many special education teachers report:
- Feeling isolated and unsupported
- Heavy Workload
- Low Pay
- Burnout
- Need for Professional Development******
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a need for 37,600 new special education teachers from 2020 to 2030 to meet growing demand.* Hiring of teachers is not increasing.
******edweek.org/teaching-learning/why-special-education-teachers-quit-and-what-schools-are-doing-about-it/2024/05
A. Mockovciak, G. McKeithan, X. Johnson, D. Grisworld and M.O’Rivera. Special Education Teacher Attrition. Glob J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2023; 11(3): 555811. DOI:10.19080/GJIDD.2A23.11.555811
ies.ed.gov/learn/blog/special-educator-shortage-examining-teacher-burnout-and-mental-health
*******BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook 2022-23 – Special Education Teachers
Why Should Parents & Teachers Care?
Educational Outcomes
- They are far less likely to enroll in a 4-year college.
- They are 11X more likely to not enroll in any school vs. enrolling in a 4-year college.
- 50% attend vocational or junior colleges vs. 18% of the non-ADHD comparison group.
- 15% hold a 4-year degree compared to 48% of the control group.
- 0.06% held a graduate degree compared to 5.4% of the control group.
Biederman, Joseph at al. (July 2012). Adult outcome of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a controlled 16-year follow-up study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 73(7):941-50.
Biederman, Joseph et al. (May 2010). How persistent is ADHD? A controlled 10-year follow-up study of boys with ADHD. Psychiatry Research 177(3):299–304.
Why Should Our Nation’s Workforce Care?
Occupational Outcomes for young adults with ADHD between the ages of 23 and 32:
- They are 11x more likely to be unemployed and not in school.
- They are 4x more likely to be in unskilled vs. clerical occupation, and 6x more likely to be in unskilled vs. professional occupations.
- 61% more likely to have been fired, compared to 43% of the comparison group.
- 33% more likely to have been laid off, compared to 13% of the comparison group.
Kuriyan, A.B., Pelham, W.E., Molina, B.S.G. et al. Young Adult Educational and Vocational Outcomes of Children Diagnosed with ADHD. J Abnorm Child Psychol 41, 27–41 (2013)
William J. et al. (2013). Mortality, ADHD, and psychosocial adversity in adults with childhood ADHD: a prospective study. Pediatrics 131(4):637-644.
Guardian Airwaves LLC is focused on changing these statistics by providing tailored education technology and career support for ADHD and neurodiverse individuals to unlock economic opportunities and remove barriers to sustained employment.
